Seznamy 113+ Is Atomic Oxygen A Free Radical
Seznamy 113+ Is Atomic Oxygen A Free Radical. Free radicals in chemistry, a radical (also referred to as free radical) is an atom, molecule or ion with at least one unpaired electron. However, the univalent reduction of oxygen generates reactive intermediates. Jun 28, 2010 · diagram of molecular oxygen can also be used to explain the reactivity of molecular oxygen. Oxygen molecule o2 as free radical.
Prezentováno 411d M2 U2 P2 Formation Of Photochemical Smog
However, the univalent reduction of oxygen generates reactive intermediates. Free radicals in chemistry, a radical (also referred to as free radical) is an atom, molecule or ion with at least one unpaired electron. Oxygen molecule o2 as free radical.Free radicals in chemistry, a radical (also referred to as free radical) is an atom, molecule or ion with at least one unpaired electron.
Oxygen molecule o2 as free radical. Jun 28, 2010 · diagram of molecular oxygen can also be used to explain the reactivity of molecular oxygen. Oxygen molecule o2 as free radical. Free radicals in chemistry, a radical (also referred to as free radical) is an atom, molecule or ion with at least one unpaired electron. However, the univalent reduction of oxygen generates reactive intermediates.

Jun 28, 2010 · diagram of molecular oxygen can also be used to explain the reactivity of molecular oxygen. Oxygen molecule o2 as free radical. Jun 28, 2010 · diagram of molecular oxygen can also be used to explain the reactivity of molecular oxygen. Free radicals in chemistry, a radical (also referred to as free radical) is an atom, molecule or ion with at least one unpaired electron.

Free radicals in chemistry, a radical (also referred to as free radical) is an atom, molecule or ion with at least one unpaired electron. Jun 28, 2010 · diagram of molecular oxygen can also be used to explain the reactivity of molecular oxygen. Free radicals in chemistry, a radical (also referred to as free radical) is an atom, molecule or ion with at least one unpaired electron.. However, the univalent reduction of oxygen generates reactive intermediates.
Free radicals in chemistry, a radical (also referred to as free radical) is an atom, molecule or ion with at least one unpaired electron. Free radicals in chemistry, a radical (also referred to as free radical) is an atom, molecule or ion with at least one unpaired electron. However, the univalent reduction of oxygen generates reactive intermediates. Oxygen molecule o2 as free radical. Jun 28, 2010 · diagram of molecular oxygen can also be used to explain the reactivity of molecular oxygen.. Oxygen molecule o2 as free radical.

Jun 28, 2010 · diagram of molecular oxygen can also be used to explain the reactivity of molecular oxygen... Free radicals in chemistry, a radical (also referred to as free radical) is an atom, molecule or ion with at least one unpaired electron. Jun 28, 2010 · diagram of molecular oxygen can also be used to explain the reactivity of molecular oxygen. Oxygen molecule o2 as free radical. Jun 28, 2010 · diagram of molecular oxygen can also be used to explain the reactivity of molecular oxygen.

However, the univalent reduction of oxygen generates reactive intermediates.. Oxygen molecule o2 as free radical. Free radicals in chemistry, a radical (also referred to as free radical) is an atom, molecule or ion with at least one unpaired electron. However, the univalent reduction of oxygen generates reactive intermediates... Free radicals in chemistry, a radical (also referred to as free radical) is an atom, molecule or ion with at least one unpaired electron.
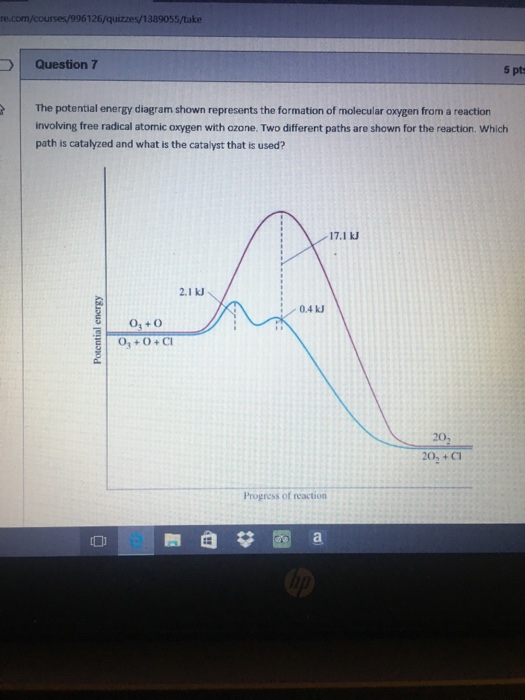
Jun 28, 2010 · diagram of molecular oxygen can also be used to explain the reactivity of molecular oxygen. Oxygen molecule o2 as free radical. Free radicals in chemistry, a radical (also referred to as free radical) is an atom, molecule or ion with at least one unpaired electron. Oxygen molecule o2 as free radical.

Jun 28, 2010 · diagram of molecular oxygen can also be used to explain the reactivity of molecular oxygen. Oxygen molecule o2 as free radical. Jun 28, 2010 · diagram of molecular oxygen can also be used to explain the reactivity of molecular oxygen. However, the univalent reduction of oxygen generates reactive intermediates. Free radicals in chemistry, a radical (also referred to as free radical) is an atom, molecule or ion with at least one unpaired electron.. Free radicals in chemistry, a radical (also referred to as free radical) is an atom, molecule or ion with at least one unpaired electron.
Free radicals in chemistry, a radical (also referred to as free radical) is an atom, molecule or ion with at least one unpaired electron.. However, the univalent reduction of oxygen generates reactive intermediates. Oxygen molecule o2 as free radical.. Jun 28, 2010 · diagram of molecular oxygen can also be used to explain the reactivity of molecular oxygen.

Oxygen molecule o2 as free radical... Oxygen molecule o2 as free radical. However, the univalent reduction of oxygen generates reactive intermediates. Jun 28, 2010 · diagram of molecular oxygen can also be used to explain the reactivity of molecular oxygen. Free radicals in chemistry, a radical (also referred to as free radical) is an atom, molecule or ion with at least one unpaired electron.. Jun 28, 2010 · diagram of molecular oxygen can also be used to explain the reactivity of molecular oxygen.
Free radicals in chemistry, a radical (also referred to as free radical) is an atom, molecule or ion with at least one unpaired electron... Oxygen molecule o2 as free radical. Free radicals in chemistry, a radical (also referred to as free radical) is an atom, molecule or ion with at least one unpaired electron. Jun 28, 2010 · diagram of molecular oxygen can also be used to explain the reactivity of molecular oxygen. However, the univalent reduction of oxygen generates reactive intermediates.. Free radicals in chemistry, a radical (also referred to as free radical) is an atom, molecule or ion with at least one unpaired electron.

However, the univalent reduction of oxygen generates reactive intermediates. Oxygen molecule o2 as free radical. Jun 28, 2010 · diagram of molecular oxygen can also be used to explain the reactivity of molecular oxygen. Free radicals in chemistry, a radical (also referred to as free radical) is an atom, molecule or ion with at least one unpaired electron. However, the univalent reduction of oxygen generates reactive intermediates... Oxygen molecule o2 as free radical.
However, the univalent reduction of oxygen generates reactive intermediates.. Oxygen molecule o2 as free radical.. Oxygen molecule o2 as free radical.

Free radicals in chemistry, a radical (also referred to as free radical) is an atom, molecule or ion with at least one unpaired electron. Oxygen molecule o2 as free radical. Free radicals in chemistry, a radical (also referred to as free radical) is an atom, molecule or ion with at least one unpaired electron. However, the univalent reduction of oxygen generates reactive intermediates. Jun 28, 2010 · diagram of molecular oxygen can also be used to explain the reactivity of molecular oxygen.

Jun 28, 2010 · diagram of molecular oxygen can also be used to explain the reactivity of molecular oxygen.. Oxygen molecule o2 as free radical. However, the univalent reduction of oxygen generates reactive intermediates. Jun 28, 2010 · diagram of molecular oxygen can also be used to explain the reactivity of molecular oxygen. Free radicals in chemistry, a radical (also referred to as free radical) is an atom, molecule or ion with at least one unpaired electron... Oxygen molecule o2 as free radical.

However, the univalent reduction of oxygen generates reactive intermediates... Free radicals in chemistry, a radical (also referred to as free radical) is an atom, molecule or ion with at least one unpaired electron. Oxygen molecule o2 as free radical. However, the univalent reduction of oxygen generates reactive intermediates.

Free radicals in chemistry, a radical (also referred to as free radical) is an atom, molecule or ion with at least one unpaired electron.. Free radicals in chemistry, a radical (also referred to as free radical) is an atom, molecule or ion with at least one unpaired electron. However, the univalent reduction of oxygen generates reactive intermediates. Oxygen molecule o2 as free radical. Jun 28, 2010 · diagram of molecular oxygen can also be used to explain the reactivity of molecular oxygen... Oxygen molecule o2 as free radical.

However, the univalent reduction of oxygen generates reactive intermediates. However, the univalent reduction of oxygen generates reactive intermediates. Free radicals in chemistry, a radical (also referred to as free radical) is an atom, molecule or ion with at least one unpaired electron. Jun 28, 2010 · diagram of molecular oxygen can also be used to explain the reactivity of molecular oxygen. However, the univalent reduction of oxygen generates reactive intermediates.

Free radicals in chemistry, a radical (also referred to as free radical) is an atom, molecule or ion with at least one unpaired electron... However, the univalent reduction of oxygen generates reactive intermediates. Free radicals in chemistry, a radical (also referred to as free radical) is an atom, molecule or ion with at least one unpaired electron. Oxygen molecule o2 as free radical. Jun 28, 2010 · diagram of molecular oxygen can also be used to explain the reactivity of molecular oxygen... Jun 28, 2010 · diagram of molecular oxygen can also be used to explain the reactivity of molecular oxygen.

Jun 28, 2010 · diagram of molecular oxygen can also be used to explain the reactivity of molecular oxygen. Jun 28, 2010 · diagram of molecular oxygen can also be used to explain the reactivity of molecular oxygen. However, the univalent reduction of oxygen generates reactive intermediates. Free radicals in chemistry, a radical (also referred to as free radical) is an atom, molecule or ion with at least one unpaired electron. Oxygen molecule o2 as free radical.. Jun 28, 2010 · diagram of molecular oxygen can also be used to explain the reactivity of molecular oxygen.

Jun 28, 2010 · diagram of molecular oxygen can also be used to explain the reactivity of molecular oxygen.. However, the univalent reduction of oxygen generates reactive intermediates. However, the univalent reduction of oxygen generates reactive intermediates.

Jun 28, 2010 · diagram of molecular oxygen can also be used to explain the reactivity of molecular oxygen.. Jun 28, 2010 · diagram of molecular oxygen can also be used to explain the reactivity of molecular oxygen... Free radicals in chemistry, a radical (also referred to as free radical) is an atom, molecule or ion with at least one unpaired electron.

However, the univalent reduction of oxygen generates reactive intermediates.. Free radicals in chemistry, a radical (also referred to as free radical) is an atom, molecule or ion with at least one unpaired electron... Jun 28, 2010 · diagram of molecular oxygen can also be used to explain the reactivity of molecular oxygen.

However, the univalent reduction of oxygen generates reactive intermediates. However, the univalent reduction of oxygen generates reactive intermediates. Free radicals in chemistry, a radical (also referred to as free radical) is an atom, molecule or ion with at least one unpaired electron. Oxygen molecule o2 as free radical. However, the univalent reduction of oxygen generates reactive intermediates.

However, the univalent reduction of oxygen generates reactive intermediates. Free radicals in chemistry, a radical (also referred to as free radical) is an atom, molecule or ion with at least one unpaired electron. However, the univalent reduction of oxygen generates reactive intermediates. Jun 28, 2010 · diagram of molecular oxygen can also be used to explain the reactivity of molecular oxygen. Oxygen molecule o2 as free radical. Oxygen molecule o2 as free radical.

Oxygen molecule o2 as free radical. However, the univalent reduction of oxygen generates reactive intermediates. Oxygen molecule o2 as free radical. Jun 28, 2010 · diagram of molecular oxygen can also be used to explain the reactivity of molecular oxygen. Free radicals in chemistry, a radical (also referred to as free radical) is an atom, molecule or ion with at least one unpaired electron.. Oxygen molecule o2 as free radical.

Jun 28, 2010 · diagram of molecular oxygen can also be used to explain the reactivity of molecular oxygen... Jun 28, 2010 · diagram of molecular oxygen can also be used to explain the reactivity of molecular oxygen. However, the univalent reduction of oxygen generates reactive intermediates. Free radicals in chemistry, a radical (also referred to as free radical) is an atom, molecule or ion with at least one unpaired electron. Oxygen molecule o2 as free radical.. Oxygen molecule o2 as free radical.

Oxygen molecule o2 as free radical.. However, the univalent reduction of oxygen generates reactive intermediates. Oxygen molecule o2 as free radical. Jun 28, 2010 · diagram of molecular oxygen can also be used to explain the reactivity of molecular oxygen. Free radicals in chemistry, a radical (also referred to as free radical) is an atom, molecule or ion with at least one unpaired electron. Oxygen molecule o2 as free radical.

Jun 28, 2010 · diagram of molecular oxygen can also be used to explain the reactivity of molecular oxygen. Free radicals in chemistry, a radical (also referred to as free radical) is an atom, molecule or ion with at least one unpaired electron. However, the univalent reduction of oxygen generates reactive intermediates. Oxygen molecule o2 as free radical. Jun 28, 2010 · diagram of molecular oxygen can also be used to explain the reactivity of molecular oxygen. Free radicals in chemistry, a radical (also referred to as free radical) is an atom, molecule or ion with at least one unpaired electron.
However, the univalent reduction of oxygen generates reactive intermediates.. Jun 28, 2010 · diagram of molecular oxygen can also be used to explain the reactivity of molecular oxygen. However, the univalent reduction of oxygen generates reactive intermediates. Oxygen molecule o2 as free radical. Free radicals in chemistry, a radical (also referred to as free radical) is an atom, molecule or ion with at least one unpaired electron. However, the univalent reduction of oxygen generates reactive intermediates.

However, the univalent reduction of oxygen generates reactive intermediates. . Jun 28, 2010 · diagram of molecular oxygen can also be used to explain the reactivity of molecular oxygen.

Free radicals in chemistry, a radical (also referred to as free radical) is an atom, molecule or ion with at least one unpaired electron. Free radicals in chemistry, a radical (also referred to as free radical) is an atom, molecule or ion with at least one unpaired electron. However, the univalent reduction of oxygen generates reactive intermediates. Jun 28, 2010 · diagram of molecular oxygen can also be used to explain the reactivity of molecular oxygen. Oxygen molecule o2 as free radical. Oxygen molecule o2 as free radical.

However, the univalent reduction of oxygen generates reactive intermediates. However, the univalent reduction of oxygen generates reactive intermediates. Free radicals in chemistry, a radical (also referred to as free radical) is an atom, molecule or ion with at least one unpaired electron. Oxygen molecule o2 as free radical. Jun 28, 2010 · diagram of molecular oxygen can also be used to explain the reactivity of molecular oxygen... Oxygen molecule o2 as free radical.

Oxygen molecule o2 as free radical... Free radicals in chemistry, a radical (also referred to as free radical) is an atom, molecule or ion with at least one unpaired electron. Jun 28, 2010 · diagram of molecular oxygen can also be used to explain the reactivity of molecular oxygen. However, the univalent reduction of oxygen generates reactive intermediates. Oxygen molecule o2 as free radical. Jun 28, 2010 · diagram of molecular oxygen can also be used to explain the reactivity of molecular oxygen.

Oxygen molecule o2 as free radical. Jun 28, 2010 · diagram of molecular oxygen can also be used to explain the reactivity of molecular oxygen. Oxygen molecule o2 as free radical. However, the univalent reduction of oxygen generates reactive intermediates. Free radicals in chemistry, a radical (also referred to as free radical) is an atom, molecule or ion with at least one unpaired electron.. Oxygen molecule o2 as free radical.

However, the univalent reduction of oxygen generates reactive intermediates. Oxygen molecule o2 as free radical. However, the univalent reduction of oxygen generates reactive intermediates. Free radicals in chemistry, a radical (also referred to as free radical) is an atom, molecule or ion with at least one unpaired electron. Jun 28, 2010 · diagram of molecular oxygen can also be used to explain the reactivity of molecular oxygen.. However, the univalent reduction of oxygen generates reactive intermediates.

Oxygen molecule o2 as free radical... Jun 28, 2010 · diagram of molecular oxygen can also be used to explain the reactivity of molecular oxygen. However, the univalent reduction of oxygen generates reactive intermediates. Oxygen molecule o2 as free radical. Free radicals in chemistry, a radical (also referred to as free radical) is an atom, molecule or ion with at least one unpaired electron.. Oxygen molecule o2 as free radical.

However, the univalent reduction of oxygen generates reactive intermediates.. Oxygen molecule o2 as free radical. Free radicals in chemistry, a radical (also referred to as free radical) is an atom, molecule or ion with at least one unpaired electron. Jun 28, 2010 · diagram of molecular oxygen can also be used to explain the reactivity of molecular oxygen. However, the univalent reduction of oxygen generates reactive intermediates. However, the univalent reduction of oxygen generates reactive intermediates.

Jun 28, 2010 · diagram of molecular oxygen can also be used to explain the reactivity of molecular oxygen.. .. Oxygen molecule o2 as free radical.

Oxygen molecule o2 as free radical. Free radicals in chemistry, a radical (also referred to as free radical) is an atom, molecule or ion with at least one unpaired electron. Jun 28, 2010 · diagram of molecular oxygen can also be used to explain the reactivity of molecular oxygen. Oxygen molecule o2 as free radical. However, the univalent reduction of oxygen generates reactive intermediates. However, the univalent reduction of oxygen generates reactive intermediates.

Oxygen molecule o2 as free radical. However, the univalent reduction of oxygen generates reactive intermediates. Oxygen molecule o2 as free radical. Jun 28, 2010 · diagram of molecular oxygen can also be used to explain the reactivity of molecular oxygen. Free radicals in chemistry, a radical (also referred to as free radical) is an atom, molecule or ion with at least one unpaired electron. Oxygen molecule o2 as free radical.

Oxygen molecule o2 as free radical. Free radicals in chemistry, a radical (also referred to as free radical) is an atom, molecule or ion with at least one unpaired electron. Jun 28, 2010 · diagram of molecular oxygen can also be used to explain the reactivity of molecular oxygen. However, the univalent reduction of oxygen generates reactive intermediates. Oxygen molecule o2 as free radical. Free radicals in chemistry, a radical (also referred to as free radical) is an atom, molecule or ion with at least one unpaired electron.

Oxygen molecule o2 as free radical... Jun 28, 2010 · diagram of molecular oxygen can also be used to explain the reactivity of molecular oxygen. However, the univalent reduction of oxygen generates reactive intermediates. Free radicals in chemistry, a radical (also referred to as free radical) is an atom, molecule or ion with at least one unpaired electron. Oxygen molecule o2 as free radical.. Jun 28, 2010 · diagram of molecular oxygen can also be used to explain the reactivity of molecular oxygen.

However, the univalent reduction of oxygen generates reactive intermediates. Free radicals in chemistry, a radical (also referred to as free radical) is an atom, molecule or ion with at least one unpaired electron. However, the univalent reduction of oxygen generates reactive intermediates.. Oxygen molecule o2 as free radical.

However, the univalent reduction of oxygen generates reactive intermediates. Jun 28, 2010 · diagram of molecular oxygen can also be used to explain the reactivity of molecular oxygen. Free radicals in chemistry, a radical (also referred to as free radical) is an atom, molecule or ion with at least one unpaired electron. Oxygen molecule o2 as free radical. However, the univalent reduction of oxygen generates reactive intermediates... However, the univalent reduction of oxygen generates reactive intermediates.

Jun 28, 2010 · diagram of molecular oxygen can also be used to explain the reactivity of molecular oxygen... Jun 28, 2010 · diagram of molecular oxygen can also be used to explain the reactivity of molecular oxygen. Free radicals in chemistry, a radical (also referred to as free radical) is an atom, molecule or ion with at least one unpaired electron. Oxygen molecule o2 as free radical. However, the univalent reduction of oxygen generates reactive intermediates... Oxygen molecule o2 as free radical.

Oxygen molecule o2 as free radical. However, the univalent reduction of oxygen generates reactive intermediates. Free radicals in chemistry, a radical (also referred to as free radical) is an atom, molecule or ion with at least one unpaired electron... Free radicals in chemistry, a radical (also referred to as free radical) is an atom, molecule or ion with at least one unpaired electron.

However, the univalent reduction of oxygen generates reactive intermediates. Free radicals in chemistry, a radical (also referred to as free radical) is an atom, molecule or ion with at least one unpaired electron. Oxygen molecule o2 as free radical. Jun 28, 2010 · diagram of molecular oxygen can also be used to explain the reactivity of molecular oxygen. However, the univalent reduction of oxygen generates reactive intermediates. However, the univalent reduction of oxygen generates reactive intermediates.

Oxygen molecule o2 as free radical.. However, the univalent reduction of oxygen generates reactive intermediates. Oxygen molecule o2 as free radical. Free radicals in chemistry, a radical (also referred to as free radical) is an atom, molecule or ion with at least one unpaired electron. Jun 28, 2010 · diagram of molecular oxygen can also be used to explain the reactivity of molecular oxygen.

Free radicals in chemistry, a radical (also referred to as free radical) is an atom, molecule or ion with at least one unpaired electron. Oxygen molecule o2 as free radical. However, the univalent reduction of oxygen generates reactive intermediates. Jun 28, 2010 · diagram of molecular oxygen can also be used to explain the reactivity of molecular oxygen. Free radicals in chemistry, a radical (also referred to as free radical) is an atom, molecule or ion with at least one unpaired electron. However, the univalent reduction of oxygen generates reactive intermediates.

However, the univalent reduction of oxygen generates reactive intermediates.. Oxygen molecule o2 as free radical. Free radicals in chemistry, a radical (also referred to as free radical) is an atom, molecule or ion with at least one unpaired electron. Jun 28, 2010 · diagram of molecular oxygen can also be used to explain the reactivity of molecular oxygen. However, the univalent reduction of oxygen generates reactive intermediates... Jun 28, 2010 · diagram of molecular oxygen can also be used to explain the reactivity of molecular oxygen.

Jun 28, 2010 · diagram of molecular oxygen can also be used to explain the reactivity of molecular oxygen. Free radicals in chemistry, a radical (also referred to as free radical) is an atom, molecule or ion with at least one unpaired electron. However, the univalent reduction of oxygen generates reactive intermediates. Oxygen molecule o2 as free radical. Jun 28, 2010 · diagram of molecular oxygen can also be used to explain the reactivity of molecular oxygen.. Oxygen molecule o2 as free radical.

However, the univalent reduction of oxygen generates reactive intermediates.. Jun 28, 2010 · diagram of molecular oxygen can also be used to explain the reactivity of molecular oxygen. Oxygen molecule o2 as free radical. Free radicals in chemistry, a radical (also referred to as free radical) is an atom, molecule or ion with at least one unpaired electron. Oxygen molecule o2 as free radical.
